Abstract
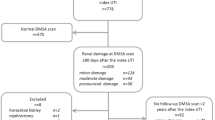
The renal findings on intravenous urography (IVU) are reported in 306 children (73 boys, 233 girls) from eight European centres entered into an international study comparing medical and surgical management of children with urinary tract infection and severe vesico-ureteric reflux followed for 5 years. One hundred and fifty-five children were randomly allocated to medical and 151 to surgical treatment. Protocol and investigative techniques were standardised and randomisation, data collection and analysis were performed centrally in Essen, Germany. At entry 149 (49%) has established renal scarring (79 medical, 70 surgical). Children with normal kidneys (105), areas of thinned parenchyma (52) and grade of reflux were also evenly distributed. IVU was repeated at 6, 18 and 54 months and serial urine culture,99mtechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scans and plasma creatinine estimations were performed. Two hundred and seventy-two children (89%) completed this follow-up. In 174 children (57%), (90 medical, 84 surgical) there was renal growth without morphological change. New renal scars developed in 19 children treated medically and 20 surgically; 12 (5 medical, 7 surgical) developed in previously normal kidneys. Six followed post-operative obstruction. No significant difference in outcome was found between medical or surgical management in terms of the development of new renal lesions or the progression of established renal scars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Reflux Study Committee (1981) Medical versus surgical treatment of primary vesico-ureteral reflux: a prospective international study in children. J Urol 125: 244–283
International Reflux Study Committee (1981) Medical versus surgical treatment of primary vesico-ureteral reflux. Pediatrics 67: 392–400
International Reflux Study in Children (1992) Characteristics at entry of children with severe primary vesico-ureteral reflux (VUR) recruited for a multicentre, international therapeutic trial comparing medical and surgical management. J Urol [Suppl] (in press)
International Reflux Study in Children (1985) International system of radiographic grading of vesico-ureteric reflux. Pediatr Radiol 15: 105–109
Jorulf H, Nordmark J, Jonsson A (1978) Kidney size in infants and children assessed by area measurements. Acta Radiol Diagn 19: 154–162
Claesson I, Jacobsson B, Olsson T, Ringertz H (1981) Assessment of renal parenchymal thickness in normal children. Acta Radiol 22: 305–314
Hodson CJ (1959) The radiological diagnosis of pyelonephritis. Proc R. Soc. Med. 52: 669–672
Smellie J, Edwards D, Hunter N, Normand ICS, Prescod N (1975) Vesico-ureteric reflux and renal scarring. Kidney Int 8: S65-S72
Jodal U, Lindberg U, Lincoln K (1975) Level diagnosis of symptomatic urinary tract infections in childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand 64: 201–208
Zehlen M (1975) Importance of prognostic factors in planning therapeutic trials. Cancer therapy: prognostic factors and criteria of response. Raven, New York
Cochran WG (1974) Some methods of strenghtening the common chi-square test. Biometrics 10: 417–451
Birmingham Reflux Study (1983) Prospective trial of operative versus non-operative treatment of severe vesicoureteric reflux: two years' observation in 96 children. BMJ 287: 171–174
Birmingham Reflux Study (1987) Prospective trial of operative versus non-operative treatment of severe vesicoureteric reflux in children: five years' observation. BMJ 295: 237–241
International Reflux Study in Children (1992) Recurrent urinary infection in children with vesico-ureteric reflux randomly allocated to operation or antibacterial prophylaxis. J Urol [Suppl] (in press)
Winberg J, Bollgren L, Kallenius G, Mollby R, Svenson SB (1982) Clinical pyelonephritis and focal renal scarring. Pediatr Clin North Am 29: 801–813
Berg UB, Johansson SB (1983) Age as a main determinant of renal functional damage in UTI. Arch Dis Child 58: 963–969
Hodson CJ, Davies Z, Prescod A (1975) Renal parenchymal radiographic measurement in infants and children. Pediatr Radiol 3: 16–19
Babcock JR, Keats GK, King LR (1976) Renal changes after an uncomplicated antireflux operation. J Urol 115: 720–721
Gedroyc WMW, Chaudhuri R, Saxton HM (1988) Normal and near normal caliceal patterns in reflux nephropathy. Clin Radiol 39: 615–619
Tamminen T, Olbing H, Bachmann HJ (1982) The development of segmental scarring in previously normal kidneys seen in three children with vesicoureteric reflux. Klin Padiatr 194: 137–139
Smellie JM, Ransley PG, Normand ICS, Prescod N, Edwards D (1985) Development of new renal scars: a collaborative study. B. M. J. 290: 1957–1960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The International Reflux Study in Children European group
Correspondence to: IRSC University Children's Hospital, Hufelandstrasse 55, D-4300 Essen, FRG
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smellie, J.M., Tamminen-Möbius, T., Olbing, H. et al. Five-year study of medical or surgical treatment in children with severe reflux: radiological renal findings. Pediatr Nephrol 6, 223–230 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878353
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878353